Use ABC codes to classify your parts based on the value (number or margin) of the stock transactions. The regular ABC classification is as follows:
The advantage of classifying your parts according to the ABC analysis is that you can handle the different types of parts in the most efficient way. For example, you could choose to count the stock of 'A' parts more often (because they have a greater turnover), and you could set a higher minimum stock for 'A' parts. As 'A' parts are responsible for a large part of your turnover, you never want to be out of stock.
To classify your parts as 'A', 'B' or 'C' parts, use the Determine ABC code process in the Parts module.
APP stands for 'average purchase price'. See also Stock valuation.
If you are using the 'Average purchase price' stock valuation method for a part, the stock valuation price is adjusted whenever the average purchase price is calculated. The new average purchase price will then become the new stock valuation price. When using the APP method, this stock valuation price is therefore not a fixed price as is the case when the 'Fixed valuation price' (FVP) stock valuation method is used.
An as-built structure shows how an object is composed of other objects and/or parts. It shows the object relationships on different levels.
This is all stock that is not blocked, i.e. the sum of all current stock lines minus the blocked stock minus the rejected stock.
This is the sum of all stock lines with the settings 'Blocked for issues and shipments' and 'Available for order point method and MRP'. This concerns stock that is expected to be blocked temporarily (for example, on a receipt location).
The Commission master data functionality allows you to maintain sales made through third parties, and define a corresponding remuneration structure. For example, you could specify that agents, such as intermediaries and dealers, will get a percentage of the turnover, or a fixed sum per order. In a sales order you can indicate whether the remuneration has already been paid.
'Converging' means that components from several operations are brought together in a single subsequent operation (for example: after separate operations, 4 chair legs and 1 chair seat are combined in the operation 'Assembly').
Costs such as administrative charges, transport costs and setup/adjustment costs can be registered as parts in the Parts module. These 'costs parts' can then be added to an offer or order, to enable you to charge these costs to a customer.
To see whether a part is a costs part, open the Parts form, and then check the General tab. If the part is a costs part, the value of the Part type field is 'Costs'.
This is the sum of all stock lines.
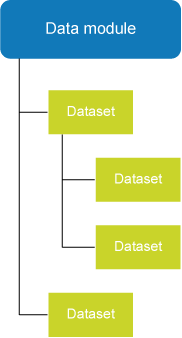
Every FastReport report is assigned a data module, which contains one or more datasets. A dataset includes SQL information as to which data will be retrieved from the database. The SQL code can also call a stored procedure.
A data module can contain more than one dataset. The datasets within a data module are interrelated, and within this structure, various master-detail branches are possible:

A dataset includes SQL information as to which data will be retrieved from the database. The SQL code can also call a stored procedure. Datasets are added to data modules:

You can then use the data modules for your FastReport reports.
Parts always have a destination, i.e. a location where there is a demand for the parts. Possible destinations in Isah are:
On 'destination locations', you can specify the origins of the parts required. This process is called 'specification'. Specifications are always expressed in quantities (values such as length, width, and height are copied from the destination location).
A destination can have more than one origin. For instance, some of the parts sold under a particular order may come from production, some from stock, and some may have been purchased.
'Diverging' means that components worked in one operation are separated and sent to different subsequent operations (for example: out of a total of 10 sawn shelves, 6 shelves will be subjected to the operation 'Red paint', and 4 shelves will be subjected to the operation 'Yellow paint').
Bedrijven die met hun import- of exportwaarde onder de vastgestelde drempelwaarde blijven, zijn vrijgesteld van het doen van een statistische opgave. De drempel wordt voor import en export afzonderlijk vastgesteld; het kunnen verschillende bedragen zijn. Een bedrijf dat op het gebied van import boven de vastgestelde drempelwaarde uitkomt, maar voor export niet, is alleen opgaveplichtig voor de import. Zie voor meer informatie en de actuele drempelwaarden www.cbs.nl.
A dummy, such as a dummy part or a dummy customer, does not contain specific information and can be used for a different item each time, for example for a different part or a different customer.
For example, if you often produce once-only parts, it would not be practical to register them all in the Parts module. This would create an inconveniently large variety of parts. Instead of registering these parts individually, create one dummy part to use for one-off parts. Then add the dummy to the offer, order or production file when a customer asks for a one-off part. Each time you use the dummy, you can add different information, such as another description or another calculation. If a dummy part does eventually become a standard product, you can create a new part for it, and copy the calculation from the production file to the new part.
The economic stock includes all stock lines, minus reservations, and plus receipts: Current stock minus Reserved for sales/production plus Planned purchase/production receipts
Entities are important components in Isah, for which you want to register a wide range of details, such as customers, production files, parts, equipment and sales orders.
FIFO (First In, First Out) is a warehouse management technique where the oldest goods leave the warehouse first. When FIFO is used as an issue sequence in Isah (Parts form, Logistics tab), and stock replenishment purchases are made, the stock is registered as at the receipt date.
You can choose to schedule operations based on either infinite or finite capacity. When scheduling based on finite capacity, the load of previously planned orders is taken into account. This planning method is more accurate than planning based on infinite capacity. An operation is scheduled based on the available capacity as well as the number of hours to plan per day. Any days with available capacity will be filled by the same operation for another order.
The free stock is all stock that is available and not blocked minus the reserved stock.
This is the sum of all stock lines that are available and not blocked: the nettable stock minus the blocked stock.
A part added as a functional BOM is usually an option that can be used in more than one finished product. As an example, this could be the braking system for a car. The braking system is comprised of a number of components and can be mounted in a wide range of cars. The components of the braking system are located in various parts of the car: one part is mounted near the tires, another part is fitted in the chassis, etcetera. It is therefore difficult to separate the braking system as a function from the finished product.
To be able to process and handle such functions separately, register them in the Parts module with their own calculation. If a customer orders a car and opts for this braking system, you add its functional BOM to the calculation of the car.
To see whether a part is a functional BOM, open the Parts module, Parts form, General tab. If the part is a functional BOM, the value in the Part type field is 'Functional BOM'.
Note: A functional BOM is not the same as a semi-finished product: semi-finished products are separate components, but a feature such as a braking system cannot be built separately from the car it will be part of.
FVP stands for 'fixed valuation price'. See also Stock valuation.
To use the 'Fixed valuation price' stock valuation method for a part, use the FVP/APP field on the Financial tab of the Parts form in the Parts module to specify the fixed price at which the stock of the part must be valued.
The FVP is used when posting stock additions or deductions as a result of:
Note: If Isah is linked to a financial application, a journal entry is created in the following situations:
De Gecombineerde Nomenclatuur (GN) is onderdeel van de Europese douanewetgeving. Het uitgangspunt van de GN is dat alle goederen ter wereld onder een bepaalde code van de GN moeten kunnen worden ingedeeld.
Een overzicht van de goederencodes is opgenomen in IDEP.
Gecombineerde Nomenclatuur
De code van een artikel volgens de Gecombineerde Nomenclatuur (GN).
Intracommunautaire levering: uitvoer naar een EU/lidstaat.
Intracommunautaire verwerving: invoer uit een EU-lidstaat.
You can choose to schedule operations based on either infinite or finite capacity. Infinite planning is useful for making a quick and rough planning. The available capacity and the number of hours to plan per day for the operation will be taken into account. This may result in overload, however, because each order is scheduled as if no other orders have been scheduled for the operation yet.
Een onderneming die de drempel ICV en/of de drempel ICL overschrijdt, is informatieplichtig. De informatieplichtige is verantwoordelijk voor de gegevens die aan het CBS worden geleverd, ook indien deze gegevens door een derde (de zogenaamde derde aangever, bijvoorbeeld een expediteur) aan het CBS worden toegezonden. De informatieplichtige wordt geïdentificeerd door zijn BTW-nummer.
Op 1 januari 1993 kwam de Interne Markt binnen de EU tot stand. Hierdoor vervielen de douaneformaliteiten voor de handel binnen de EU, en daarmee verviel ook de mogelijkheid om handelsstatistieken samen te stellen aan de hand van deze douaneformulieren. De behoefte aan statistische informatie over de handel tussen EU-landen bleef echter bestaan. Daarom is door de EU het zogenaamde Intrastat-stelsel in het leven geroepen. Ondernemers dienen hun handelsgegevens nu rechtstreeks door te geven aan de statistiekdiensten in de lidstaten. Voor Nederland is dat het CBS. Het doorgeven van de statistische informatie dient te gebeuren via de webapplicatie IDEP, dat door het CBS gratis verstrekt wordt.
Het Intrastat-stelsel omvat de gehele goederenhandel binnen de EU (= Intrahandel), met uitzondering van de douanegoederen. Gegevens over de handel met landen buiten de EU worden samengesteld aan de hand van douaneopgaves.
De Intrastat-regeling verplicht alle bedrijven in Nederland om gegevens met betrekking tot de in– of uitvoer van goederen binnen de EU door te geven aan het CBS, als het bedrag van in– of uitvoer een bepaalde drempelwaarde overschrijdt. Deze drempelwaarde vindt u op de website van het CBS: www.cbs.nl.
An example of a line operation is a machine cycle comprising multiple operations that take place in succession. The operations that are part of a line operation are specified on the Grouped operations form.
Long lead-time items are parts with a long delivery time that need to be ordered, but of which the production file in which they will be used is not known yet. This prevents a regular order to be created in Isah, but often there is no time to wait for the production file. To solve this problem, Isah provides the option of ordering these long lead-time items under a special production order for long lead-time items.
MRP stands for Materials Requirement Planning.
If you are using the MRP method, the requirement for a part is calculated during the execution of the Run MRP process. The part requirements are determined based on the customer orders and forecasts. The MRP method is very similar to the time-phased order point method. Instead of calculating the requirement for just one part, however, the MRP method calculates the requirements for multiple parts from various part levels (semi-finished products).
As soon as a requirement for the part has been established, the part will appear on the purchase requirement. If it is a production part to be produced under a production order, a production file is created. Then the part calculation is copied and subsequently performed. When performing this calculation, the MRP process continues up to the lowest MRP level.
You are recommended to use the MRP stock control method when a part is used as a semi-finished product in a large number of parts. MRP is the most accurate stock control method, because calculations are performed for various calculation levels.
The Isah navigation pane groups are located in the lower-left corner of the main menu:
The navigation pane groups allow you to quickly navigate to related forms within a particular functional area. The navigation pane group of the CRM functional area, for example, contains all forms relating to customers, suppliers, employees, and more. The subdivision into navigation pane groups enables you to open all modules and forms that are relevant to your functional area in one go.
Some functional areas are displayed on a bar, while others are shown in buttons on the toolbar. This has to do with the size of the windows and the form. When you use the mouse to resize the windows, the buttons are moved to the bars or moved off the bars, as the case may be.
This is the available stock, i.e. the sum of all stock lines with the setting 'Available for order point method and MRP'.
An object is a unique part for which you can provide service. An object can also be a location, however, such as a building or a ship you want to refer to. An object itself can, in turn, also consist of objects. For example, a factory may house various machines that comprise an engine. The hierarchical relationship between the objects Factory, Machines, and Engines can be displayed in an as-built structure.
The order level is calculated based on the expected usage of the part and the minimum stock that serves as 'safety stock'. The order level must be sufficient to bridge the time remaining until the next delivery, taking into consideration any fluctuations in the expected usage. These fluctuations are absorbed by the minimum stock.
If you are using the Order point method, the requirement of a specific part is calculated based on the date the economic stock of the part will reach a pre-determined stock level (order level). When a requirement for the part is established (Economic stock < Order level), a purchase requirement is created, to ensure that the economic stock will reach the order level as a minimum.
The purchase requirement has the current date as the order date; the receipt date is the current date plus the delivery time.
The period for which the requirement is calculated is determined by the Planning horizon specified for the part, or by the To date set for the Create purchase requirements for stock parts process.
Use the order point method for stock parts of which the requirements are covered by the stock. The stock control method to be used for a part is registered on the Logistics tab of the Parts form.
Parts always have an origin. Origins are locations from which parts are available. Possible origins in Isah are:
On 'origin locations', you can specify the destinations of the parts. This process is called 'assignment'. Assignments are always expressed in quantities (values such as length, width, and height are copied straight from the origin location).
An origin can have more than one destination. For instance, some of the parts produced under a particular production order may be used for a sales order, while other parts may be added to the stock.
Purchase order lines are an exception in this respect, as they can only have one destination.
The term 'phantom' is used to refer to phantom part lines. A phantom line is a line that has been added to a calculation only for informational purposes. Phantoms are used if you want to include the calculation of a semi-finished product in the calculation of the finished product in which it is used, but still want to see which calculation components belong to the semi-finished product and which belong to the finished product. The components of the semi-finished product will then refer to the phantom line, which only mentions the relevant semi-finished product.
The setting Show phantom determines wether or not the phantom is visible in the calculation.
![]()
A preset displays a particular selection of data. It is a user-dependent, predefined filter on the List tab of various forms. On many forms, you can choose from several default presets, or you can manually define multiple presets for each form. To create you own presets, some knowledge of SQL is required.
You could use a preset, for example, for the Parts form in the Parts module. Whereas this form usually contains a great many records, your work may involve only a small number of parts. If that is the case, you can use a preset to specify the parts that are relevant to you. By activating this preset from within the Parts form, the form will only display those parts that meet the conditions of your preset.
The next time you open the Parts form, it will show only the parts specified by the preset you used last. To see another selection, select another preset.
Presets are faster than filters, as filters are applied on the client (the workstation itself), whereas presets are dealt with on the server. When using filters, all data are retrieved from the server, and the filtering process takes place on the client computer. If you are using presets, the data are filtered on the server, and only the filter results are displayed on your screen.
Note: Before users can use default presets, each user or user group must first be given rights to the default presets.
The Isah production modules are Preliminary Costing, Work Preparation, Planning, Production, and Actual Costing.
Production parts are finished products or semi-finished products you produce yourself and of which you can include the composition in a product calculation. You can offer and sell finished products to customers based on offers and orders. Semi-finished products can be used in other semi-finished or finished products, or you can sell semi-finished products directly to a customer (as a spare part, for example). Production parts appear on the purchase requirement if the stock of the parts is insufficient. In this case, it will be a purchase requirement of the 'Production order' type (because you produce the parts yourself).
To see whether a part is a production part, open the Parts form, General tab. If the part is a production part, the value in the Part type field is 'Production part'.
Purchase parts are parts you purchase from a supplier. Purchase parts can be used as components of semi-finished products or finished products, but they can also be sold straight from stock to a customer. A purchase part is displayed on the purchase requirement if there is insufficient stock of the purchase part, or if it must be ordered to order.
Purchase parts can contain a calculation, for example if you do the engineering work for the part yourself, and therefore instruct your supplier how the part is to be made. This is a hybrid form of regular purchasing and outsourcing.
To see whether a part is a purchase part, open the Parts form, General tab. If the part is a purchase part, the value in the Part type field is 'Purchase part'.
A purchase requirement lists parts, equipment, or external operations that, because of an order or stock requirement, should be ordered or produced. After correcting or changing a purchase requirement where necessary, you can 'promote' it to a purchase offer, purchase order, or internal production order (only for parts).
This stock does not have a specific name in Isah, but all stock with the settings 'Blocked for issues and shipments' and NOT 'Available for order point method and MRP' can be considered to be 'Rejected' stock.
The SE factor is a multiplication factor that can be used by companies offering sheltered employment (SE). This factor is used when converting the commercial operation times to the times used in the case of sheltered employment.
In Isah, an SE company creates offers and establishes preliminary costing figures based on the same labor, machine, and overhead rates as regular businesses offering similar services. They also use the same operation standards (capacity and times) as regular businesses (business practice standards or 'BPS'). As a result, the range of parts offered by an SE company is similar to that of a regular company in terms of sales prices and production costs.
However, because of the staffing nature at a sheltered workshop, different capacity standards and hourly rates are used in the production calculation when orders are entered in Isah. In general, this means that the hourly rates are lower because of subsidies and alternative pay scales, and that the operation times are longer and the capacity is lower.
The SE factor ensures that the operation times are converted, and you do not have to make these adjustments to the production orders by hand.
Service orders are sales orders with an alternative origin: they are created under a service contract or a service notification.
If you register services such as service and maintenance in the Parts module, you can add them to an offer or order to invoice the relevant costs to a customer. You can include the component parts of a service, such as call-out charges, spare parts, and assembly, in a calculation. You can also post hours against the service in the Time Registration module (for example, 'Assembly hours' when delivering a machine).
To see whether a part is a service, open the Parts module, Parts form, General tab. If the part is a service, the value in the Part type field is 'Service'.
Various stock terms are used in the Isah software. For all definitions, the stock is the sum of the stock lines for each part.
All stock lines |
|
All stock lines with the setting 'Available for order point method and MRP'. |
|
Blocked: |
All stock lines with the settings 'Blocked for issues and shipments' and 'Available for order point method and MRP'. This concerns stock that is expected to be blocked temporarily (for example, on a receipt location). |
Rejected: |
This stock does not have a specific name in Isah, but all stock with the settings 'Blocked for issues and shipments' and NOT 'Available for order point method and MRP' can be considered to be 'Rejected' stock. |
Available: |
Current stock minus Blocked stock minus Rejected stock |
Freely available: |
Nettable stock minus Blocked stock |
Nettable stock minus Blocked stock minus Stock reserved for sales/production |
|
Current stock minus Reserved for sales/production minus Planned purchase/production receipts |
In other words:
Current stock: |
All stock lines |
Nettable stock: |
All stock that is available |
Available: |
All stock that is not blocked |
Freely available: |
All stock that is available and not blocked |
Free stock: |
All stock that is available and not blocked minus Reservations |
Economic stock: |
All stock lines minus Reservations plus Receipts (current date) |
Blocked: |
All stock that is blocked |
Rejected: |
All stock that is blocked and not available |
Lastly, there are two further terms that are relevant to time-phased stock, as applicable to MRP and the time-phased order point method:
Expected stock: |
Nettable stock minus Reservations plus Receipts |
Planned stock |
Nettable stock minus Reservations plus Receipts plus Requirements |
The Part stock overview form lists all stock types for every part.
Schematic overview
|
Stock lines |
Planned purchase/production receipts |
Planned production/sales deliveries |
|||
|
Available |
Blocked |
||||
|
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
||
Current stock |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
|
Nettable stock |
+ |
|
+ |
+ |
|
|
Available stock |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
|
|
Freely available stock |
+ |
|
+ |
|
|
|
Free stock |
+ |
|
+ |
|
|
minus |
Economic stock |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
minus |
Blocked stock |
+ |
+ |
|
+ |
|
|
Rejected stock |
|
+ |
|
+ |
|
|
In Isah, stock is maintained by part. A stock line has seven features that uniquely identify the stock:
The fields marked with an asterisk (*) are mandatory.
The stock date is a distinguishing feature only if a part has a FIFO issue sequence.
When an object is assigned to a stock line, the stock line becomes unique to that object. Stock features can be used in that case, but they are not relevant for selection purposes.
In Isah, you can choose from two stock valuation methods: the method based on the fixed valuation price (FVP), or the method based on the average purchase price (APP). These methods can be used side-by-side for various part groups or parts. The procedure is as follows:
Note: Changing the fixed valuation price (FVP) or the average purchase price (APP) of a part has financial implications. The reason is that they are the prices used for stock valuation. If Isah is linked to financial software, a journal entry is created when the FVP or APP is changed.
A stored procedure is a collection of predefined SQL statements. They are executed directly in the database. Provided that you have the appropriate rights, you can open the stored procedure in a SQL tool.
Successors are operations or jobs that are dependent on another, earlier operation or job. As they are linked to the earlier operation or job, the progress of that earlier operation or job affects their own start and end date. If the earlier operation or job overruns, the successors will automatically move up in time.
You can configure an object (such as an engine) as a component of a target object (a car). This relationship is visible in the as-built structure.
In Isah, a time bucket is a period of one week (Monday to Sunday) that is used for MRP and the time-phased order point method to determine the requirement. Planned replenishments and requirements are always considered in one-week periods.
Examples
Part without stock:
If you are using the Time-phased order point method, the requirement for a part is calculated by checking on a week-by-week basis when the expected stock of the part will reach a particular stock level (minimum stock). When a requirement for the part is established (expected stock < minimum stock), a purchase requirement is created, to ensure that the planned stock will reach the minimum level as a minimum.
The receipt date for the purchase requirement is the Monday of the week in which the part is required; the order date is the receipt date minus the delivery time.
The period for which the requirement is calculated is determined by the Planning horizon specified for the part, or by the To date set for the Create purchase requirements for stock parts process.
Use the time-phased order point method for stock parts you want to replenish based on actual requirements. The stock control method to be used for a part is registered on the Logistics tab of the Parts form.
The WIP location feature is used to register the storage of parts purchased or produced to order. As the items will not be part of your stock, a separate location is required. This location is called the 'Work in Progress (WIP) location'.